Lucifer
Lucifer
AKA Phosphoros, Heosphoros, Hêlêl / Heylel

Titles:
The Morning Star, Lord of Pride, Light-Bringer, The Fallen, Lord of the Air, Son of the Dawn, Member of the Unholy Trinity
Culture:
Greco-Roman / Jewish / Christian / Islamic
Kin:
Aurora (mother), Cephalus (father), Ceyx (son), Beelzebub (son, in some traditions)
Appearance:
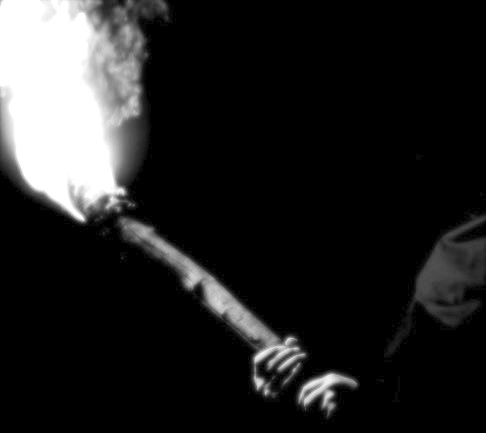
As the Morning Star, Lucifer is portrayed as an angelic male figure bearing a torch. He is also depicted in some cases as a winged, haloed youth dispensing light from various devices.
Purpose/Role:
- Described in the Tanakh as one whose excessive pride and ambition result in his banishment from the kingdom of heaven (Isaiah 14:12)
- Early Latin translators of the Hebrew text applied the term "lucifer" to the individual referenced in Isaiah
- The majority of modern English translations now use the term "morning star" however
- Now regarded as the archetypal fallen angel, as Isaiah 14:12-15 has become the de facto source for the fallen angel motif
- As a member of the Unholy Trinity (alongside Astaroth and Beelzebub), Lucifer is among the most powerful demons in Hell, taking second place only to Satan himself
- Many Christians have interpreted Lucifer's fall as the principal example of the consequences of arrogance and insubordination, going as far as to identify him with the personification of evil
- As a result, his name has come to be associated with egotism and the opposition of God's will
- Some claim for example that the serpent who seduces Eve in the Garden of Eden is in fact Lucifer in disguise, while others claim it is Satan
- This has led to the popularization of "Lucifer" as a synonym for Satan, despite the two being separate figures
- For a more detailed analysis of the differences between Lucifer and Satan, click here.
- As a result, his name has come to be associated with egotism and the opposition of God's will